Building gRPC Server Note CRUD API with node.js
Published at Sep 2, 2018
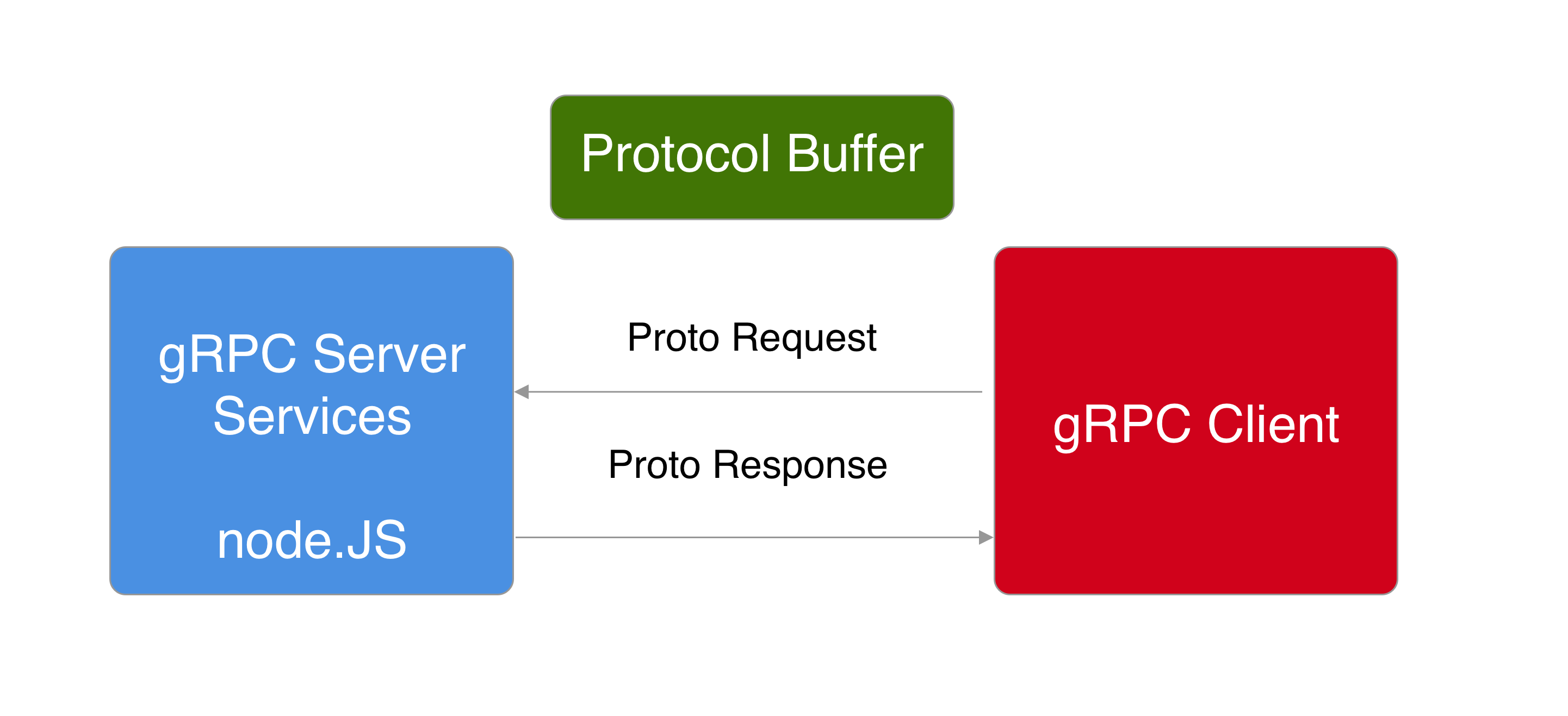
gRPC is a remote procedure call framework developed by Google that has been gaining interests among many software developers that were developing microservices in recent years because its open source, language neutral, compact binary size, HTTP/2 support, and cross platform compatibility. According to Google:
gRPC is a language-neutral, platform-neutral remote procedure call (RPC) framework and toolset developed at Google. It lets you define a service using Protocol Buffers, a particularly powerful binary serialization toolset and language. It then lets you generate idiomatic client and server stubs from your service definition in a variety of languages
In a nutshell, gRPC server application distributes sets of service methods that can be directly call by the gRPC clients across different machines and platforms with the same parameter and return type. gRPC uses Protocol Buffer binary serialization for the request and response message format between the server and client. It is more compact than JSON and converts nicely to the native language data type using the Protocol Buffer compiler. The compiler accepts proto file that is declared using the Interface Definition Language and compiles it to the target language specified. This compact binary format is very well suited for mobile application.
In this article, we will build a simple gRPC Server with node.js that provides services that provide the create, read, update, delete method for Note. We also will create gRPC node.js Client that calls the method from the gRPC server. The full source code for the project is also available at the project GitHub repository at alfianlosari/node-grpc-server-note-crud.
What we will build
Here are the things that we will building through this article:
- node.js project using npm and required package dependencies for gRPC
- proto file that declare our gRPC Message and Service for Note CRUD
- gRPC Server using node.js
- List rpc service method to get list of notes
- gRPC Client using node.js
- Insert rpc service method to insert new note
- Delete rpc service method to delete existing note by id
Create NPM Project and Add Dependencies
To start, create a new folder for the project and perform npm init to initialize the NPM project. There are 2 dependencies that our project are going to use, so install them from the shell.
- grpc: official node.js gRPC Library
- uuid: library for generating unique UUID based on timestamp
npm install --save grpc
npm install --save uuid
Declaring Proto File and Note Message
Inside the project directory, create new file called notes.proto. This is the file where we declare our Protocol Buffer Message and gRPC Service. The first thing we want to add inside the proto file is the Note Message that will represent the Note Model object. The Note Model has 3 scalar value fields, id (String), title (String), and content (String). We also need to add unique numbered tags for each field. We declare the syntax to use the proto3 version of the protocol buffer language which is the current latest version.
syntax = "proto3";
message Note {
string id = 1;
string title = 2;
string content = 3;
}
Implement and Run gRPC Server Locally
Next, we want to implement our node.js gRPC Server. Create a new file called index.js which will be the main entry point of our application. Inside we import the grpc module, then we use the grpc load method passing the path of our notes.proto so it can be loaded by the grpc module.
Then we instantiate grpc Server object and bind it to our localhost with the port of 50051, and passing Server Credential insecure object for our current development testing. Finally we invoke the start method of the server to start our gRPC server.
const grpc = require('grpc')
const notesProto = grpc.load('notes.proto')const server = new grpc.Server()server.bind('127.0.0.1:50051', grpc.ServerCredentials.createInsecure())
console.log('Server running at http://127.0.0.1:50051')
server.start()
Try to run the app by executing node index.js. The shell should print out the text server running at our localhost port to the console.
Create Our List RPC method to Fetch Notes
The first RPC method that we will create for our NoteService is the List method. The List method accepts an Empty Message and returns NoteList Message. We need to declare the NoteList message, it only has one repeated Note field called notes. Repeated means that the field is a type of List or an Array. We also create an Empty Message as the empty stub for empty request or empty response for a method.
syntax = "proto3";
service NoteService {
rpc List (Empty) returns (NoteList) {}
}
message Empty {}message Note {
string id = 1;
string title = 2;
string content = 3;
}
message NoteList {
repeated Note notes = 1;
}
Then we need to add NoteService to our gRPC server inside the index.js file. We invoke the server addService method passing the NoteService service from the notes proto object, the second parameter accepts an object that we will assign the list key with the value of function handler that will be invoked when the client calls the List method. It has 2 parameters, call and callback. The call is the request from the Client while the callback is a function we will invoke to return the response to the Client.
For the simplicity of this article, we will use in memory array to store our Note object. We declare the notes array containing our initial note objects. Inside the list function handler we just call the completion callback passing the notes as the second argument. The first argument accepts an error object to indicate if there is an error to the client, in our case we just pass null.
// index.js
const grpc = require('grpc')
const notesProto = grpc.load('notes.proto')
const notes = [
{ id: '1', title: 'Note 1', content: 'Content 1'},
{ id: '2', title: 'Note 2', content: 'Content 2'}
]
const server = new grpc.Server()
server.addService(notesProto.NoteService.service, {
list: (_, callback) => {
callback(null, notes)
},
})
server.bind('127.0.0.1:50051', grpc.ServerCredentials.createInsecure())
console.log('Server running at http://127.0.0.1:50051')
server.start()
Restart the server to apply our new List service.
Create gRPC Client to call our List gRPC Service Method
To call our gRPC Server method and see the response, we will create a gRPC node.js Client. Create a new file called client.js. Inside, we import the gRPC module, then load the notes.proto file and instantiate the Client using the NoteService object passing the localhost and the port of our gRPC server. We also pass insecure credentials for our development testing. At last we exports the client object in this module so it can be imported by other Client method we will implement.
// client.js
const grpc = require('grpc')
const PROTO_PATH = './notes.proto'
const NoteService = grpc.load(PROTO_PATH).NoteService
const client = new NoteService('localhost:50051',
grpc.credentials.createInsecure())
module.exports = client
To invoke the list method using our gRPC client, create a new file called get_notes.js. Inside, we import the client from the client.js, then we invoke the list method passing empty object as the first argument, the second argument is the callback handler that will be invoked when the call result response is received. It has 2 parameters, error and the response. We check if the error is null then just print the response to the console using the console.log.
// get_notes.js
const client = require('./client')
client.list({}, (error, notes) => {
if (!error) {
console.log('successfully fetch List notes')
console.log(notes)
} else {
console.error(error)
}
})
Make sure the server is already running, then execute the node get_notes.js from the shell to call our List RPC method and see the notes printed to the console.
Create Insert RPC Service to Create New Note
The next method we will implement is the Insert method. This method accepts a Note Message as the request parameter and return the inserted Note Message as the response.
// notes.proto
syntax = "proto3";
service NoteService {
rpc List (Empty) returns (NoteList) {}
rpc Insert (Note) returns (Note) {}
}
....
We will add the insert method function handler inside the index.js file. Import the uuid/v1 module at the top of the file, this will be used to generate unique uuid timestamp for the note to be inserted to our notes array. Inside the insert function handler, we get the note from the request, then assign the note id using the uuidv1() method. We push the new note to our notes array then at last invoke the completion callback passing the new note as the second parameter.
// index.js
...
const uuidv1 = require('uuid/v1')
...
server.addService(notesProto.NoteService.service, {
...,
insert: (call, callback) => {
let note = call.request
note.id = uuidv1()
notes.push(note)
callback(null, note)
}
})
...
To invoke the insert method, create a new file called insert_note.js. Inside we just import our client, then invoke the insert method passing an object containing the hardcoded text and content value of the note we want to create in the server. Inside the completion callback, we just check if there is no error, then we print the created response note from the server using console.log.
// insert_note.js
const client = require('./client')
let newNote = {
title: "New Note",
content: "New Note content"
}
client.insert(newNote, (error, note) => {
if (!error) {
console.log('New Note created successfully', note)
} else {
console.error(error)
}
})
Make sure the server is already running with the latest added method, then execute the node insert_note.js from the shell to call our Insert RPC method and see the created notes printed to the console.
Create Delete RPC Service to Delete Existing Note
The last method we will implement is the Delete method. This method accepts a NoteRequestId Message as the request parameter and return the Empty Message as the response. We create the NoteRequestId Message with single id (String) as the field.
// notes.proto
syntax = "proto3";
service NoteService {
rpc List (Empty) returns (NoteList) {}
rpc Insert (Note) returns (Note) {}
rpc Delete (NoteRequestId) returns (Note) {}
}
....
message NoteRequestId {
string id = 1;
}
We will update our gRPC Server inside index.js to add the delete method function handler. Inside the handler we find the index of existing note using the id from request NoteRequestId object inside our notes array. If the note index is found, we just remove the note from the array at that index using splice method.
// index.js
...
server.addService(notesProto.NoteService.service, {
...,
delete: (call, callback) => {
let existingNoteIndex = notes.findIndex((n) => n.id == call.request.id)
if (existingNoteIndex != -1) {
notes.splice(existingNoteIndex, 1)
callback(null, {})
} else {
callback({
code: grpc.status.NOT_FOUND,
details: "Not found"
})
}
}
})
...
To invoke the delete method, create a new file called delete_note.js. Inside we just import our client, then invoke the get method passing an object containing the id with hardcoded value of “1”. Inside the completion callback, we just check if there is no error, then we print the response note from the server using console.log.
// delete_note.js
const client = require('./client')
client.delete({ id: '1' }, (error, _) => {
if (!error) {
console.log('Note Has been successfully deleted')
} else {
console.error(error)
}
})
Conclusion
Finally Our gRPC Server that provides Note CRUD service is up and running, ready to be deployed and to distribute remote procedure call among many clients. gRPC also supports many other features such as authentication, bidirectional steaming, flow control, bindings, cancellation, and timeouts that we can explore in the future. Checkout the complete source code in the project GitHub repository for the full implementation of the Update and Get Single Note method. Keep doing the best and Happy Lifelong Learning 😋.